Body Changes as you age, deterioration and disease, combatted by Intermittent Fasting!
I have included references and links to research supporting this article
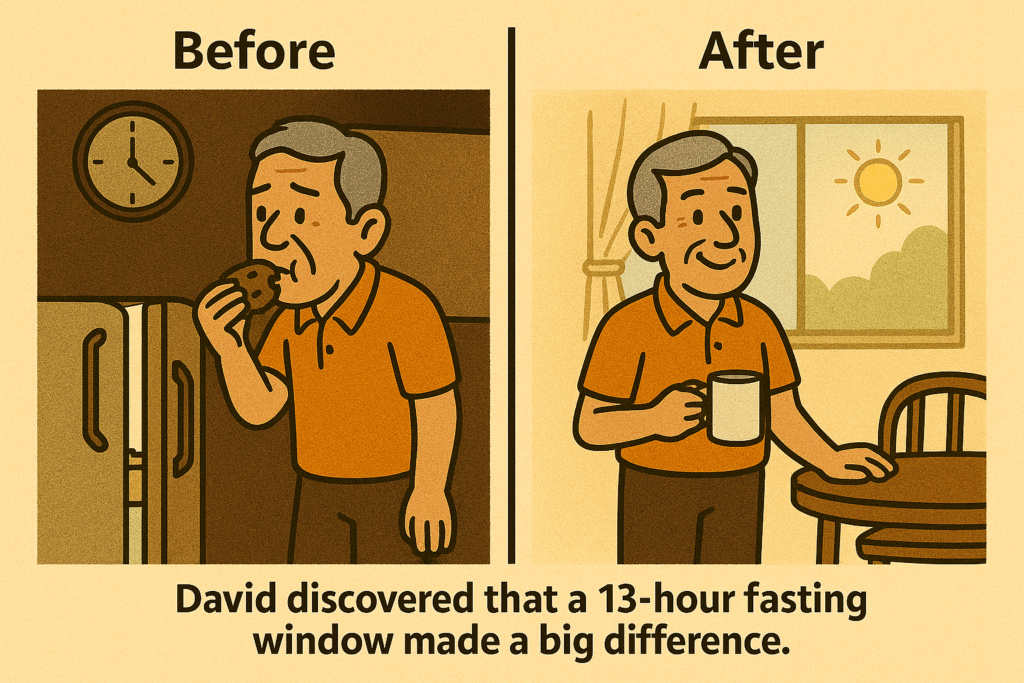
Opening Story: John’s Wake-Up Call
John, age 72, had always considered himself “reasonably healthy.” He enjoyed gardening, reading crime novels, and taking his dog on short walks. But over the last few years, he noticed changes: climbing the stairs left him winded, his trousers fit more snugly, and he often craved biscuits late at night.
At his yearly check-up, John’s doctor gently mentioned “insulin resistance.” To John, it sounded mechanical, like a car part gone rusty. What it meant was that his body wasn’t using sugar properly anymore — putting him at risk of Type 2 diabetes.
When John’s daughter suggested intermittent fasting, his first thought was: “Skip breakfast? At my age? That sounds extreme.”
But after reading that fasting was less about deprivation and more about timing, he decided to try. His first step was simple: stop eating after dinner. By morning, he had gone 12 hours without food — something he hadn’t done in decades.
Within weeks, John’s trousers fit better, his morning energy returned, and he even noticed less stiffness in his hands when pruning roses. His experience was not unique. Science is showing us that even in your 70s, fasting awakens the body’s built-in repair systems.
“John discovered fasting wasn’t about eating less — it was about eating with rhythm.”
Why the Body Changes After 70
Aging brings wisdom, patience, and perspective — but also real physical changes:
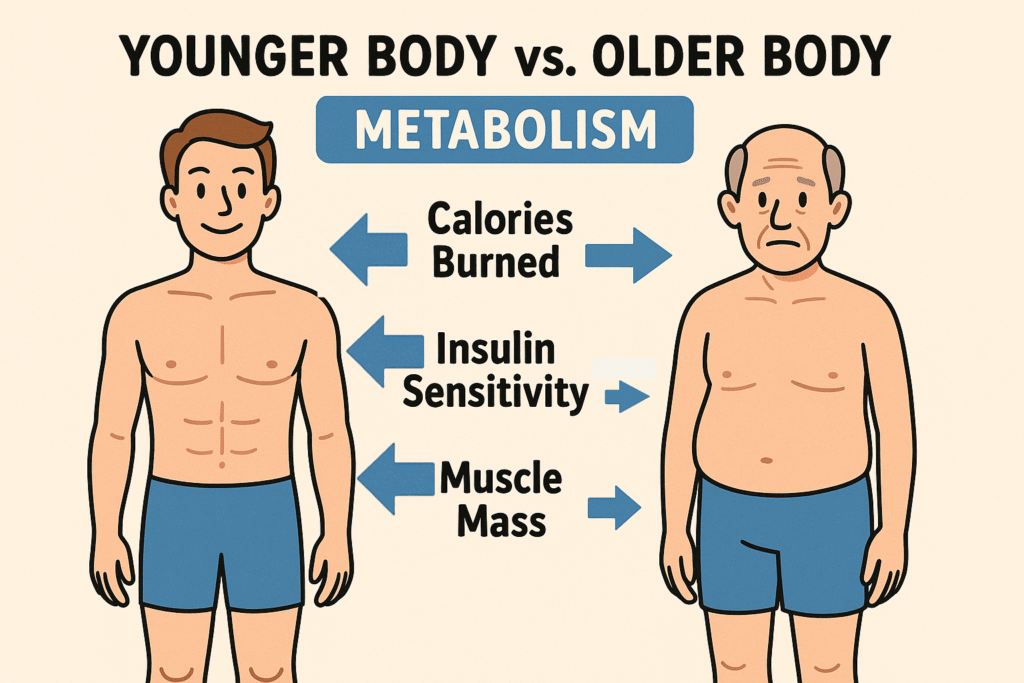
- Slower metabolism → fewer calories burned at rest.
- Reduced insulin sensitivity → blood sugar rises more easily.
- Loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) → affects strength and balance.
- Stiffer arteries → higher blood pressure risk.
- Chronic inflammation → linked to arthritis, memory decline, and heart disease.
These changes aren’t signs of failure — they are part of the natural life cycle. But fasting offers a tool to counterbalance them.
How Intermittent Fasting Helps
“Fasting is like giving your body a break from constant digestion so it can catch up on maintenance work.“
Here’s what happens during fasting hours:
- Blood sugar falls → your body starts burning fat instead of sugar.
- Insulin levels drop → cells become more responsive to it.
- Growth hormone rises → helping preserve muscle.
- Autophagy (“cellular recycling”) switches on → damaged parts of cells are cleared away.
- Inflammation markers decline → easing pressure on joints and blood vessels.
Think of fasting as a night-shift cleaning crew. When the kitchen (your body) closes for the night, the cleaners come in, scrub the floors, and take out the trash.
🔬 Research Spotlight 1: Blood Sugar & Insulin
A 2018 study in Cell Metabolism found that time-restricted eating improved insulin sensitivity and lowered fasting blood sugar in older adults.
Quote: “Time-restricted feeding improved insulin sensitivity and reduced fasting glucose in older adults.”
Takeaway for seniors:When you eat within a set window, your body handles sugar better — even at age 70 and beyond.
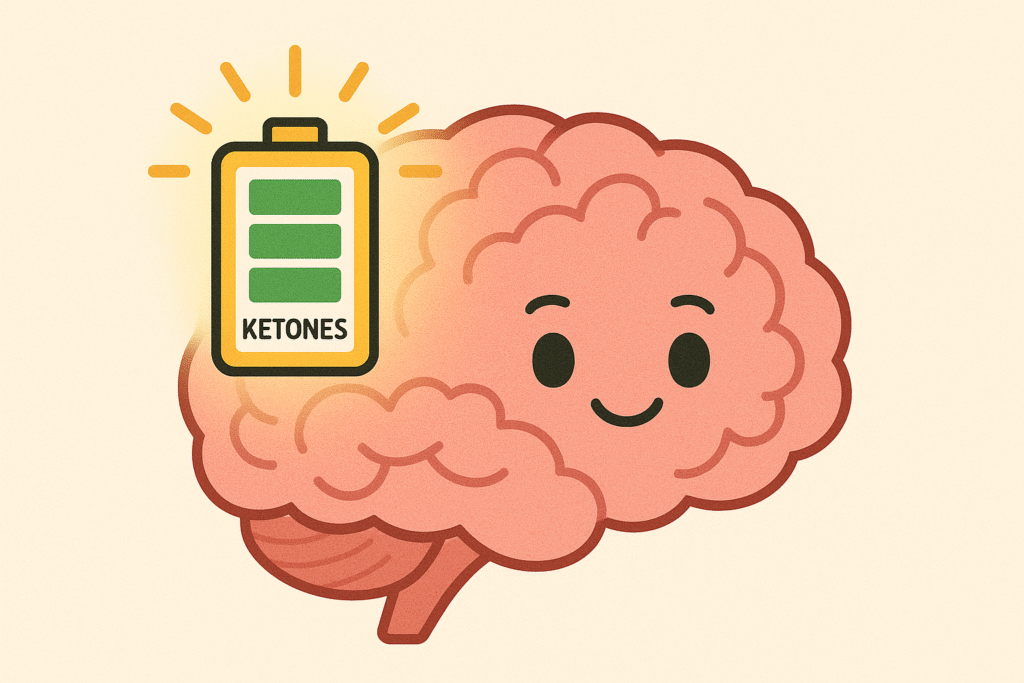
Brain Benefits of Fasting
Seniors often notice forgetfulness, “foggy” mornings, or difficulty concentrating. Fasting can help because it increases ketones — an alternative brain fuel.
Ketones act like a high-quality battery backup for the brain. They:
- Improve mental clarity.
- Reduce inflammation in brain tissue.
- Support new brain cell growth.
Some researchers believe fasting may even help delay Alzheimer’s disease progression.
🔬 Research Spotlight 2: Brain Health
A 2021 paper in The Lancet Healthy Longevity reported:
Quote: “Intermittent fasting enhances cognitive function and reduces markers of neuroinflammation in older adults.”
Takeaway:Fasting isn’t just about the waistline — it can help protect memory and focus too.
Fasting and the Heart
The heart pumps 100,000 times a day, every day. After 70, blood vessels stiffen, and heart disease risk rises.
Fasting supports cardiovascular health by:
- Lowering blood pressure.
- Reducing LDL (“bad”) cholesterol.
- Improving circulation.
- Lowering inflammation inside blood vessels.
🔬 Research Spotlight 3: Heart Benefits
A 2019 study in JAMA Internal Medicine found:
Quote: “Intermittent fasting significantly reduced systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol in older participants.”
Takeaway:Think of fasting as gentle heart medicine — without the side effects.
Fasting and Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s “fire alarm.” Helpful when you have an infection, but harmful when it’s always ringing.
Chronic inflammation is linked to:
- Arthritis
- Memory decline
- Heart disease
- Autoimmune flare-ups
During fasting, inflammatory markers drop. Seniors often notice less joint stiffness and more energy after adopting fasting.
🔬 Research Spotlight 4: Inflammation
A 2021 study in Nutrients found:
Quote: “Time-restricted eating reduced systemic inflammation markers in older adults.”
Takeaway:Less inflammation means less pain, healthier joints, and a calmer immune system.
Senior Tip Box
🟩 “Think of fasting as giving your body a daily tune-up. Just like you wouldn’t keep a car engine running all night, your body also benefits from rest.”